Why do we Model?
- Provide structure for problem solving
- Experiment to explore multiple solutions
- Furnish abstractions to manage complexity
- Reduce time-to-market for business problem solutions
- Decrease development costs
- Manage the risk of mistakes
System Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
- Waterfall effect
- Each phase flows into the next
- Plan – Analyze – Design – Implement – Support
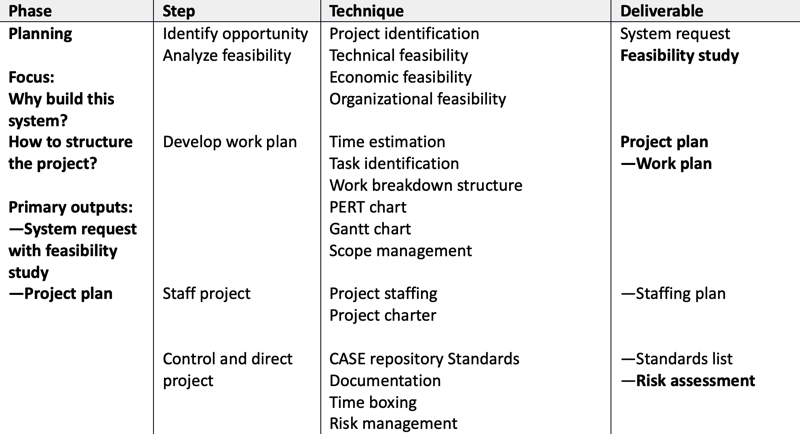
System Planning
- Identify and prioritize proposed system
- Define scope and boundary of problem
System Analysis
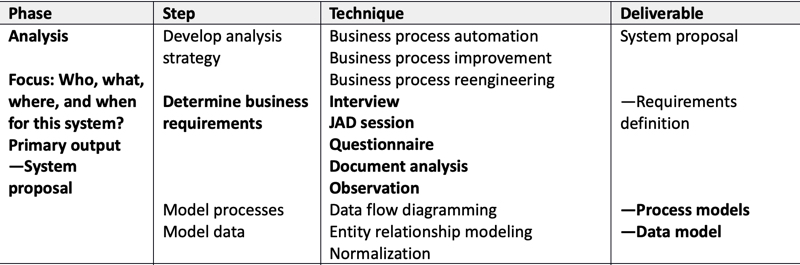
- Build a logical model of the system
- Analyze current problems, causes and effects
- Define business requirements
- Inputs: Facts and requirements
- Outputs: Business requirements document
System Design
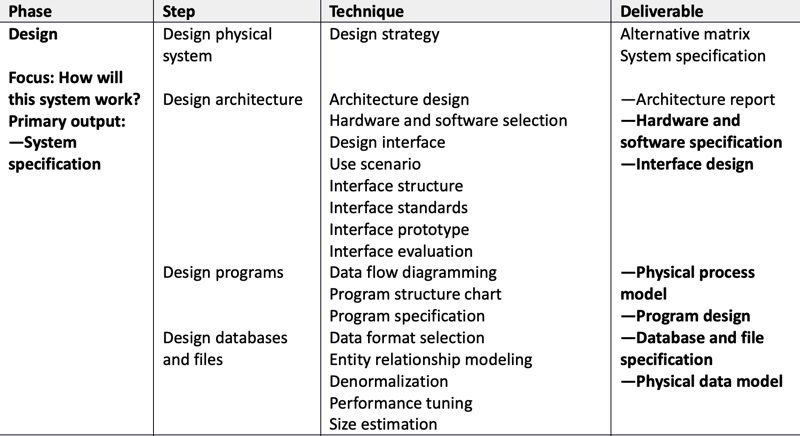
- Design the solution that meets business requirements:
- Create a physical model of the system.
- User interfaces
- Internal and external controls
- Security
- Inputs: Business requirements document
- Outputs: Technical design document
System Implementation
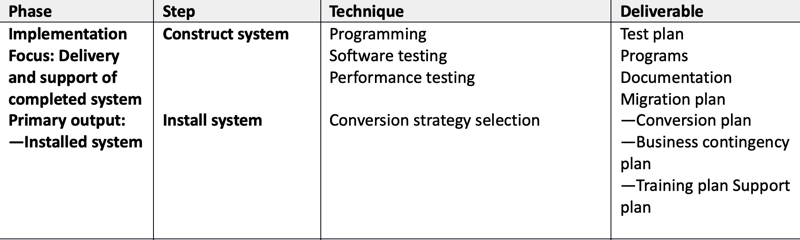
- Create new improved information system
- Input – technical design document
- Output – system delivered, end user training and documentation
- Develop conversion strategy
- Parallel, direct cutover, phased, pilot
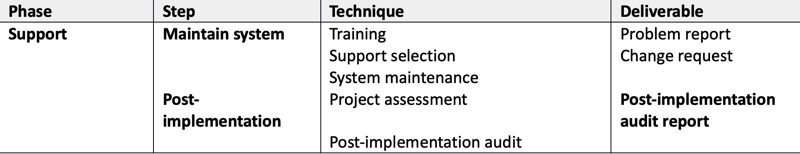
System Operation and Support
- Review implementation, refine design, implement improvements
- Maintenance of system for remainder of useful life
Systems Development Guidelines
- Follow your overall development plan
- Ensure that the users are involved from the beginning so that you get “buy in” and you fully understand their system requirements
- Listen, listen and listen!!
- Identify your major milestones for project review and assessment.
- Establish interim checkpoints between the major milestones to ensure that your project remains on schedule.
- Keep flexible with the parameters of your plan
- Provide reliable cost and benefit information.
- Graphical representation
- Business model
- Object model
- Data model
- Network model
- Process model
2. Prototyping
- Purpose to test system concepts before implementation
- Feasibility
- Requirements
- Design (Behavioral)
- Implementation (Production)
- Benefits
- Disadvantages
- Powerful software to assist systems analysts to develop and maintain information systems
- Benefits
- Easier to build software
- Increased IT productivity
- Methodologies that work
- Structured Analysis
- Object Oriented Analysis
- Joint Application Development (JAD)




