Advanced Topics - Overload Operators
Introduction
In procedural programming it is quite easy to perform mathematical operations on numerical data types. In OOP where the class contains numerical properties it becomes complex if we bring back the numerical properties and then perform the mathematical operations. Fortunatey, there is batter solution - perform the math inside the class definition.
Demo
For this demo, you will resue the Die class created earlier. You will need to modify the class to add the overload operators. The modified Die class is shown below:
namespace OverloadDemo
{
public class Die
{
private Random rnd = new Random();
//private member fields
private int _sides;
private int _faceValue;
//public Accessors & Mutators
public int Sides
{
get { return _sides; } // public Accessor
//public Mutator
set
{
if (value >= 4)
{
_sides = value;
}
else
{
throw new Exception("Invalid sides for a Die");
}
}
}//end of Sides
public int FaceValue
{
get { return _faceValue; }
set
{
if (value > 0 && value <= _sides)
{
_faceValue = value;
}
else
{
throw new Exception("Invalid face value for a Die");
}
}
}//end of FaceValue
//Constructor(s)
//Empty Constructor
public Die()
{
Sides = 6;
Roll();
}
//Greedy Constructor
public Die(int sides)
{
Sides = sides;
Roll();
}
//Class method(s)
public void Roll()
{
FaceValue = rnd.Next(1, Sides + 1);
}//end of Roll
public override string ToString()
{
//return "Sides = " + Sides + ", FaceValue = " + FaceValue;
return string.Format("Sides = {0}, FaceValue = {1}", Sides, FaceValue);
}
#region Overloaded Operators
//1. Equality
public static bool operator ==(Die a, Die b)
{
return a.FaceValue == b.FaceValue;
}
//2. Inequality
public static bool operator !=(Die a, Die b)
{
return a.FaceValue != b.FaceValue;
}
//3. Addition
public static int operator +(Die a, Die b)
{
return a.FaceValue + b.FaceValue;
}
//4. Subtraction
public static int operator -(Die a, Die b)
{
return Math.Abs(a.FaceValue - b.FaceValue);
}
#endregion
}//eoc
}//eon
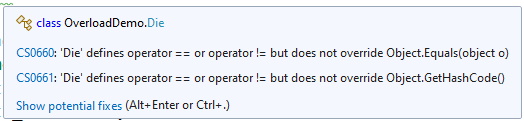
Note 1: You must have both the == and != overloads if either one is present in the class.
Note 2: there are two warnings, CS0660 and CS0661 that can be ignored.
The program code looks like:
namespace OverloadDemo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Setup();
Die a = new Die();
Die b = new Die(8);
Console.WriteLine("The two dice are:\n{0}\n{1}", a, b);
CheckForDoubles(a, b);
Console.WriteLine($" Die a + Die b = {a + b}");
Console.WriteLine($"|Die a - Die b| = {a - b}");
Console.ReadLine();
}//eom
static void CheckForDoubles(Die a, Die b)
{
//This method will check if the two dice are equal to each other
// using an overloaded operator
if (a == b)
{
Console.WriteLine("Doubles!");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("No doubles ...");
}
}//end of CheckForDoubles
static void Setup()
{
Console.Title = "Overloading Operators Demo";
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Black;
Console.BackgroundColor = ConsoleColor.White;
Console.Clear();
}//end of Setup
}//eoc
}//eon
