Advanced Topics - Collection Property
Introduction
In more advanced OOP you will come across a class that includes a property that is a collection of another class. The class diagram below is an example of this:
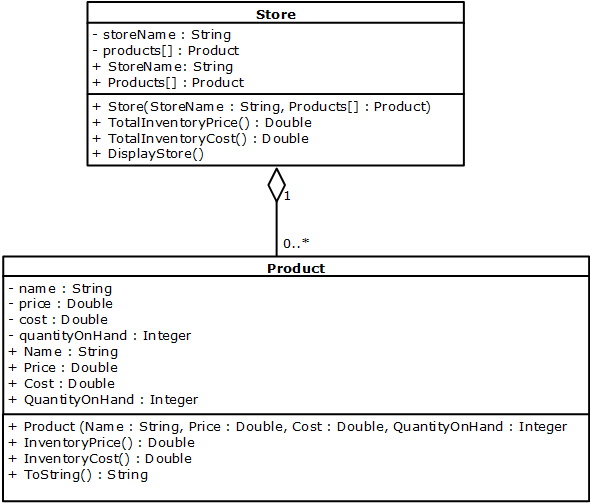
Here you see that the Store class has a property that is a collection of the Product class.
Product Class
There are 2 calculation methods in this class which take in no external parameters. In order for them to calculate, and return, a value they must have data values. Where do the data values come from? They come from the properties of the class (i.e., they are class-level methods).
namespace InventoryDemo
{
class Product
{
private string _name;
private decimal _price;
private decimal _cost;
private int _quantityOnHand;
public string Name
{
get { return _name; }
set
{
if (value.Length >= 3 && value.Length <= 20)
{
_name = value;
}
else
{
if (value.Length < 3)
{
throw new Exception("Invalid name ... must be at least 3 characters");
}
else
{
throw new Exception("Invalid name ... must not be greater than 20 characters");
}
}
}
}//eop
public decimal Price
{
get { return _price; }
set
{
if (value > 0)
{
_price = value;
}
else
{
throw new Exception("Invalid price ... must be greater than 0");
}
}
}//eop
public decimal Cost
{
get { return _cost; }
set
{
if (value > 0)
{
_cost = value;
}
else
{
throw new Exception("Invalid cost ... must be greater than 0");
}
}
}//eop
public int QuantityOnHand
{
get { return _quantityOnHand; }
set
{
if (value >= 0)
{
_quantityOnHand = value;
}
else
{
throw new Exception("Invalid quantity on hand ... must be >= 0");
}
}
}//eop
public Product(string name, decimal price, decimal cost, int quantityOnHand)
{
Name = name;
Price = price;
Cost = cost;
QuantityOnHand = quantityOnHand;
}//eom
public decimal InventoryPrice()
{
return Price * QuantityOnHand;
}//eom
public decimal InventoryCost()
{
return Cost * QuantityOnHand;
}//eom
public override string ToString()
{
return string.Format("{0,-21}{1,8:c}{2,8:c}{3,6}{4,15:c}{5,15:c}", Name, Price, Cost, QuantityOnHand, InventoryPrice(), InventoryCost());
}
}//eoc
}//eon
Store Class
Like the Product class, there are 2 calculation methods. These methods need the data values from each of the Product objects in the Products[] collection.
namespace InventoryDemo
{
class Store
{
private string _storeName;
public List<Product> Products;
public string StoreName
{
get { return _storeName; }
set
{
if (value.Length >= 3 && value.Length <= 20)
{
_storeName = value;
}
else
{
if (value.Length < 3)
{
throw new Exception("Invalid name ... must be at least 3 characters");
}
else
{
throw new Exception("Invalid name ... must not be greater than 20 characters");
}
}
}
}//eop
public Store(string storeName, List<Product> products)
{
StoreName = storeName;
Products = products;
}//eom
public decimal TotalInvntoryCost()
{
decimal totalCost = 0;
foreach(Product product in Products)
{
totalCost += product.InventoryCost();
}
return totalCost;
}//eom
public decimal TotalInventoryPrice()
{
decimal totalPrice = 0;
foreach(Product product in Products)
{
totalPrice += product.InventoryPrice();
}
return totalPrice;
}//eom
public void DisplayStore()
{
Console.WriteLine(StoreName + "\n");
Console.WriteLine("{0,-21}{1,8}{2,8}{3,6}{4,15}{5,15}", "Name", "Price", "Cost", "Qty", "Price Total","Cost Total");
foreach(Product product in Products)
{
Console.WriteLine(product);
}
Console.WriteLine("\n{0,43}{1,15:c}{2,15:c}","Totals: ", TotalInventoryPrice(), TotalInvntoryCost());
}//eom
}//eoc
}//eon
Program Class
namespace InventoryDemo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Setup();
//NOW CODE UP A STORE
try
{
string storeName = GetSafeString("Name of the store: ");
List<Product> products = new List<Product>();
AddProducts(products);
Store myStore = new Store(storeName, products);
Console.Clear();
myStore.DisplayStore();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}//eom
static void Setup()
{
Console.Title = "Store Inventory Demo";
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Black;
Console.BackgroundColor = ConsoleColor.White;
Console.Clear();
}//eom
static void AddProducts(List<Product> products)
{
char addAnother = 'Y';
string name;
decimal price, cost;
int quantityOnHand;
Product product = null;
do
{
try
{
name = GetSafeString("Product name: ");
price = GetSafeDecimal("Product price: ");
cost = GetSafeDecimal("Product cost: ");
quantityOnHand = GetSafeInt("Quantity on hand: ");
product = new Product(name, price, cost, quantityOnHand);
products.Add(product);
Console.Write("\nAdd another product (Y): ");
addAnother = char.ToUpper(char.Parse(Console.ReadLine()));
}
catch (Exception)
{
Console.WriteLine("ERROR: Input is not valid");
}
} while (addAnother == 'Y');
}//eom
#region Validation Methods
static decimal GetSafeDecimal(string prompt)
{
decimal number = 1;
bool isValid = false;
do
{
try
{
Console.Write("{0,20}", prompt);
number = decimal.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
if (number > 0)
{
isValid = true;
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("ERROR: Invalid number ... try again");
}
}
catch (Exception)
{
Console.WriteLine("ERROR: Invalid number ... try again");
}
} while (!isValid);
return number;
}//eom
static int GetSafeInt(string prompt)
{
int number = 1;
bool isValid = false;
do
{
try
{
Console.Write("{0,20}", prompt);
number = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
if (number >= 0)
{
isValid = true;
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("ERROR: Invalid number ... try again");
}
}
catch (Exception)
{
Console.WriteLine("ERROR: Invalid number ... try again");
}
} while (!isValid);
return number;
}//eom
static string GetSafeString(string prompt)
{
string name = "";
bool isValid = false;
do
{
Console.Write("{0,20}", prompt);
name = Console.ReadLine();
if(name.Length >= 3)
{
isValid = true;
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("ERROR: Name is not valid");
}
} while (!isValid);
return name;
}//eom
#endregion
}//eoc
}//eon
Testing
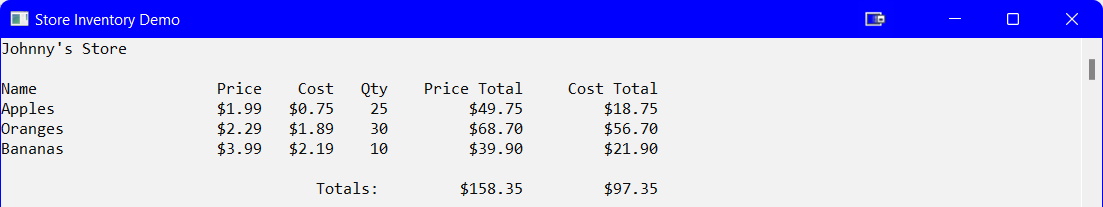
The screenshots below show the testing of:
- Entering the name of the store
- Adding products to the store
- Displaying the store inventory