Arrays - Searching
Introduction
There are two types of searches:
- Sequential: Start at the beginning of the array and examine each element, one after the other, to locate a value
- Binary: Requires a sorted array and does a Divide & Conquer approach; splits the array in halves until the value is found
A search can return:
- The value
- A Boolean
- The location in the array
- The count of how many matching items are in the array
Sequential Searches
Although the code examples below are for integer arrays, the logic is similar for an array of strings.
Sequential Search - Boolean
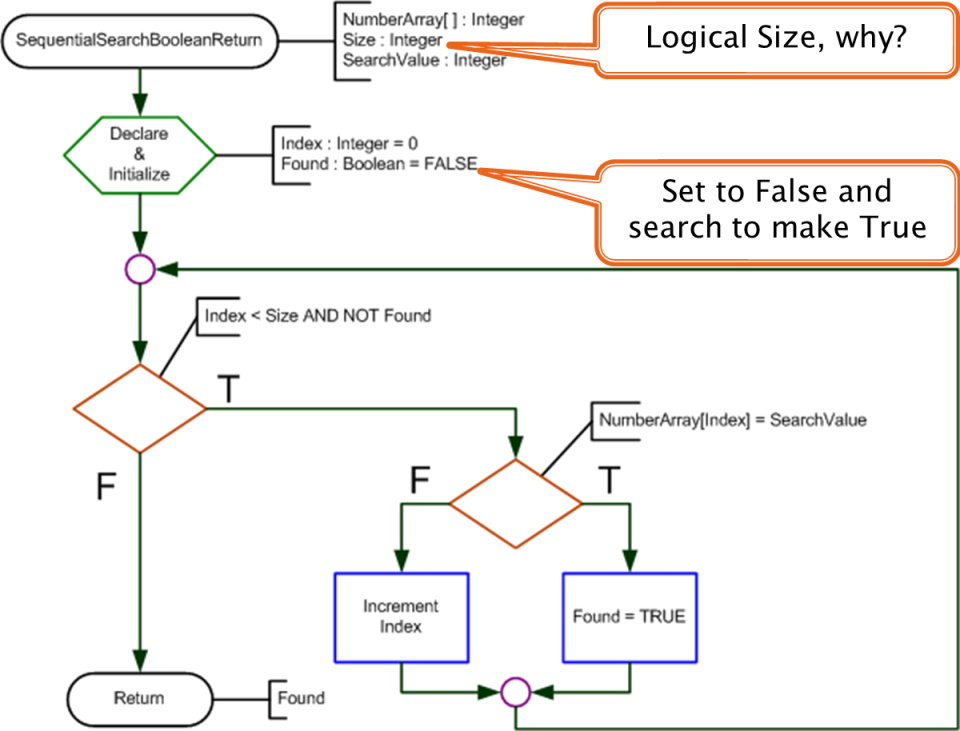
static bool SearchArrayBoolean(int[] grades, int size, int searchValue)
{
bool found = false;
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
{
if (searchValue == grades[index])
{
found = true;
index = size;
}
}
return found;
}//end of SearchArrayBoolean
Sequential Search - Location
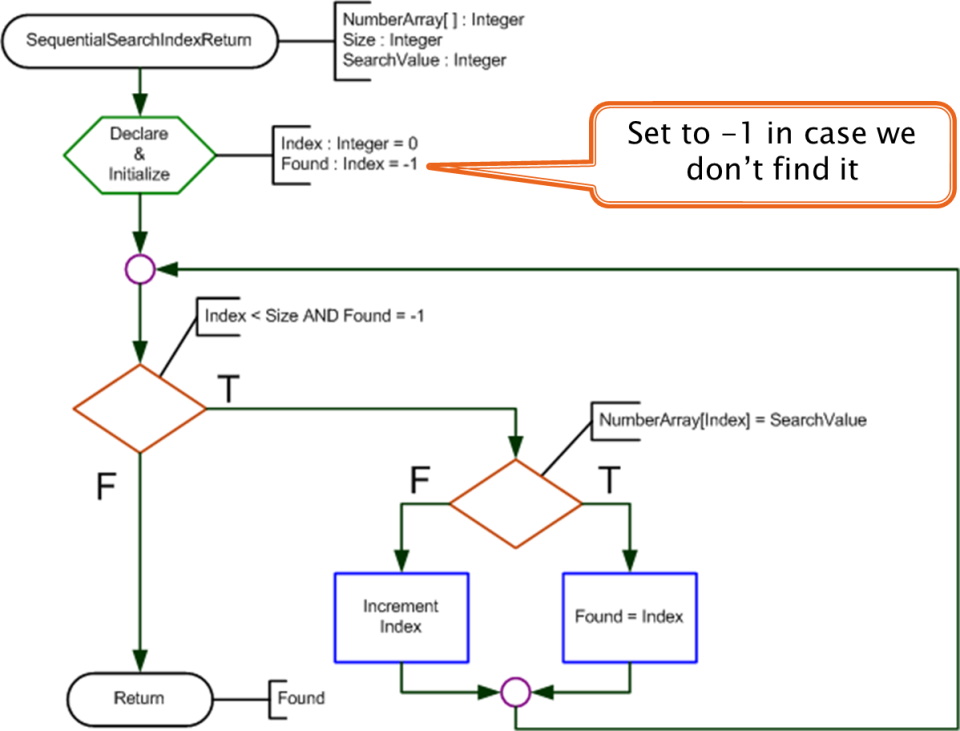
static int SearchArrayLocation(int[] grades, int size, int searchValue)
{
int location = -1; //-1 is NOT a valid index number of an array
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
{
if (searchValue == grades[index])
{
location = index;
index = size;
}
}
return location;
}//end of SearchArrayLocation
Sequential Search - Count
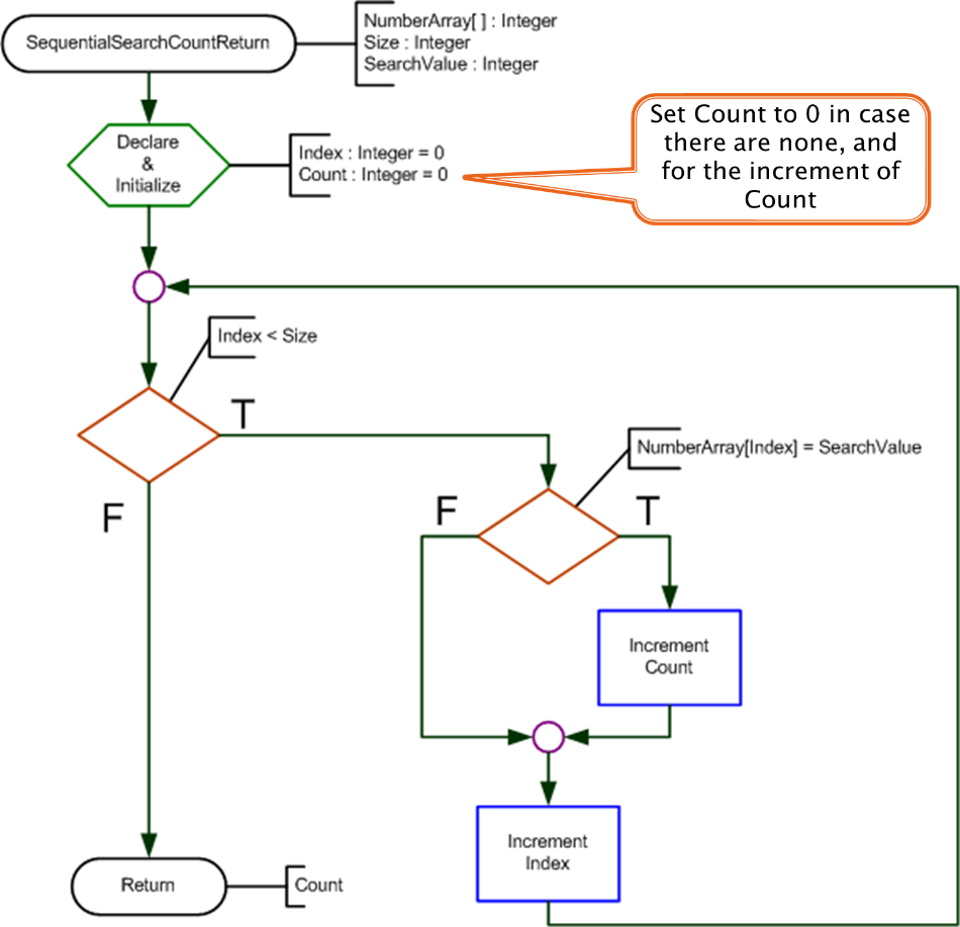
static int SearchArrayCount(int[] grades, int size, int searchValue)
{
int count = 0;
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
{
if (searchValue == grades[index])
{
count++;
}
}
return count;
}//end of SearchArrayCount
NOTE
Before coding it is important to remember that the comparison of strings is different from numerical values.
- Numbers:
if(a == b)is a valid test - Strings:
if("Allan" == "allan")is not always valid, instead useif("Allan".Equals("allan"))
Binary Search
Selection Sort
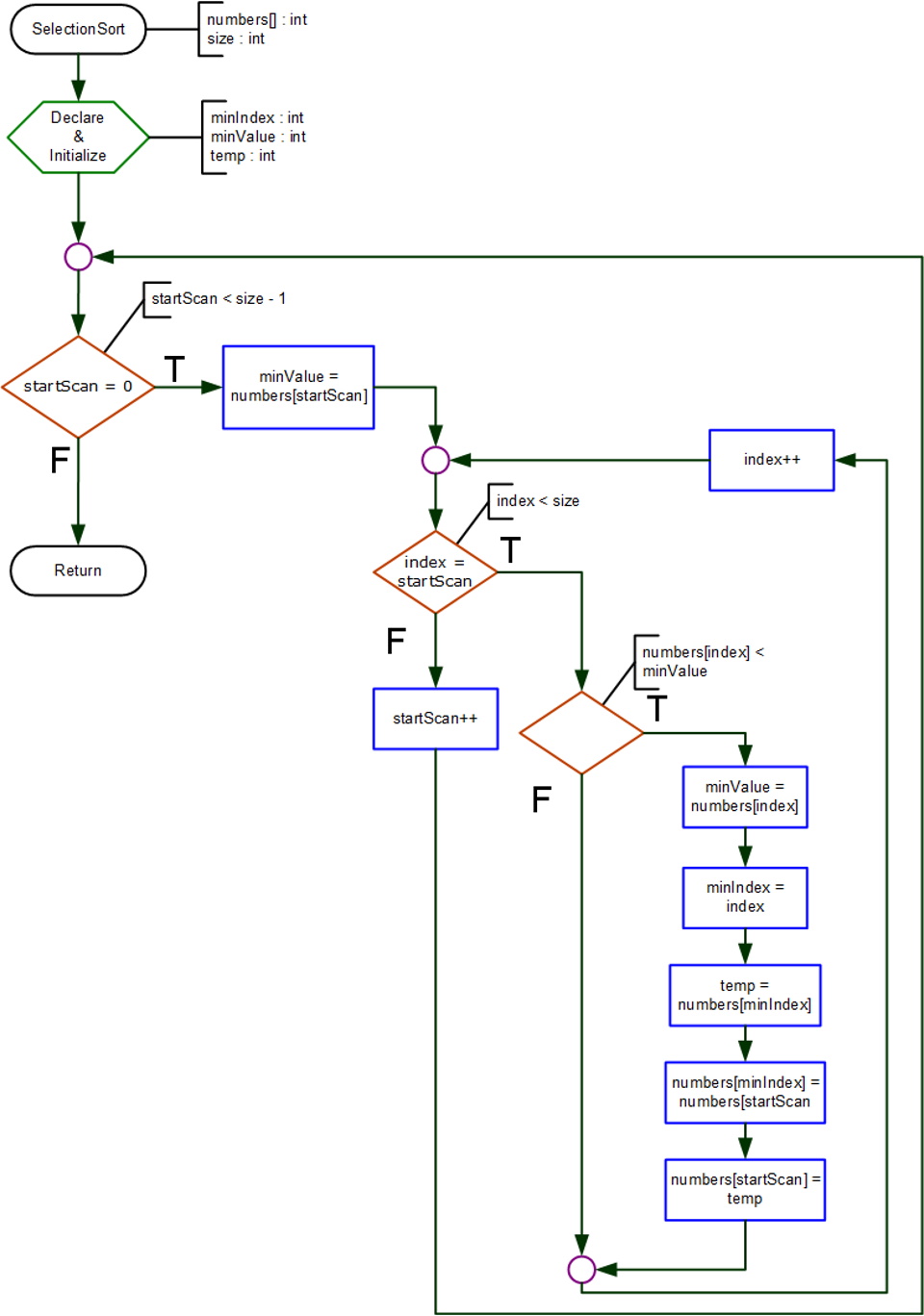
static void SelectionSort(int[] numbers, int size)
{
int minIndex, minValue;
int temp;
for (int startScan = 0; startScan < size - 1; startScan++)
{
//assume, for now, the first element has the smallest value
minValue = numbers[startScan];
//now look at the rest of the array
for (int index = startScan; index < size; index++)
{
if (numbers[index] < minValue)
{
minValue = numbers[index];
minIndex = index;
//now swap
temp = numbers[minIndex];
numbers[minIndex] = numbers[startScan];
numbers[startScan] = temp;
}//end if
}//end inner for
}//end outer for
}//end of SelectionSort
To apply this to an array of strings you could have:
static void SelectionSort(string[] names, int size)
{
int minIndex;
string temp,
minValue;
for (int startScan = 0; startScan < size - 1; startScan++)
{
//assume, for now, the first element has the smallest value
minValue = names[startScan];
//now look at the rest of the array
for (int index = startScan; index < size; index++)
{
if (names[index].ToUpper().CompareTo(minValue.ToUpper()) < 0)
{
minValue = names[index];
minIndex = index;
//now swap
temp = names[minIndex];
names[minIndex] = names[startScan];
names[startScan] = temp;
}//end if
}//end inner for
}//end outer for
}//end of SelectionSort
Binary Search
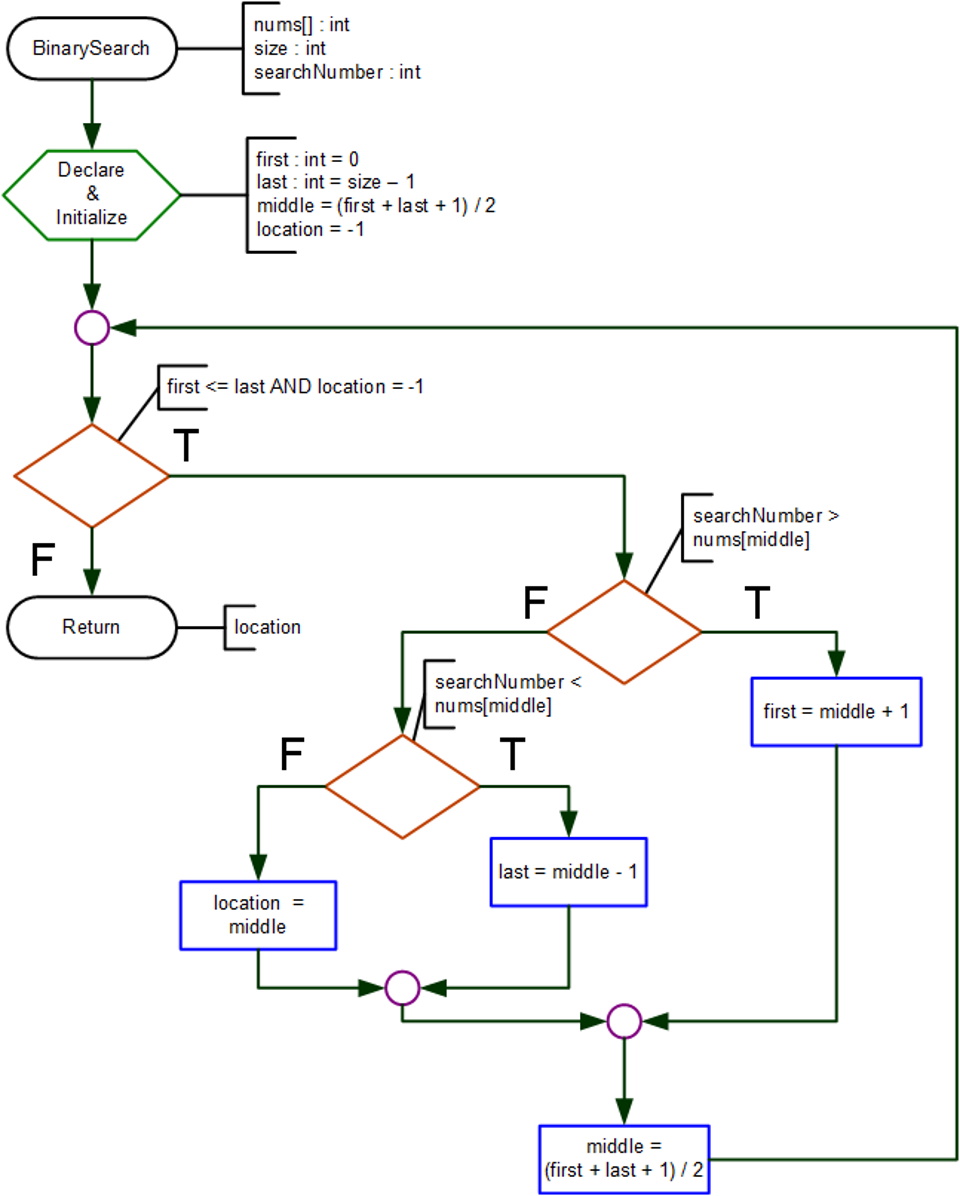
static int BinarySearch(int[] numbers, int size, int searchNumber)
{
//Ensure the array is sorted!
SelectionSort(numbers, size);
//local variables
int first = 0,
last = size - 1;
int middle = (first + last + 1) / 2;
int location = -1;
//loop
while (first <= last && location == -1)
{
if (searchNumber > numbers[middle])
{
first = middle + 1;
}
else if (searchNumber < numbers[middle])
{
last = middle - 1;
}
else
{
location = middle;
}
middle = (first + last + 1) / 2;
}
return location;
}//end of BinarySearch
Applying this technique to serach through an array of strings you could have:
static int BinarySearch(string[] names, int size, string searchName)
{
//1. Ensure the array is sorted
SelectionSort(names, size);
//2. Local scope variables
int first = 0,
last = size -1,
middle = (first + last + 1) / 2,
location = -1;
//3. Loop
while (first <= last && location == -1)
{
if (searchName.ToUpper().CompareTo(names[middle].ToUpper()) > 0)
{
first = middle + 1
}
else if (searchName.ToUpper().CompareTo(names[middle].ToUpper()) < 0)
{
last = middle -1;
}
else
{
location = middle
}
middle = (first + last + 1) / 2;
}
return location;
}//end of BinarySearch
Coding Example
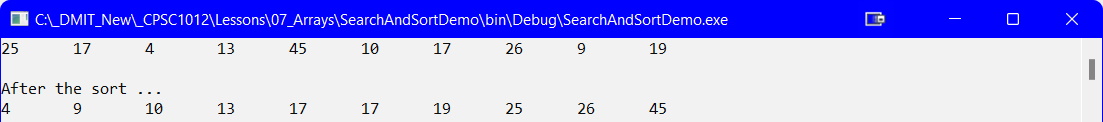
For this demo the array will be manually filled with values.
const int PhysicalSize = 10;
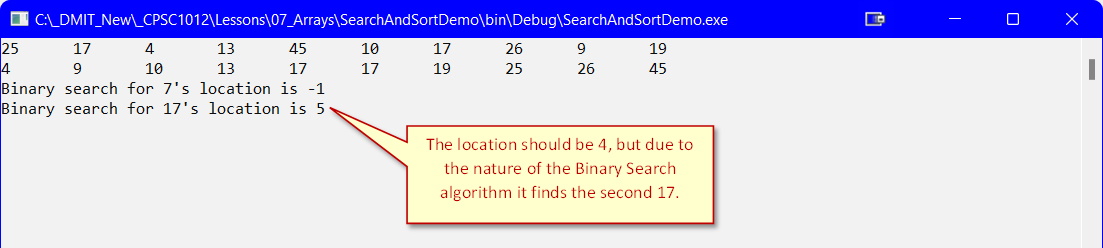
int[] numbers = { 25, 17, 4, 13, 45, 10, 17, 26, 9, 19 };
DisplayArray(numbers, PhysicalSize);
static void DisplayArray(int[] numbers, int size)
{
for(int index = 0; index < size; index++)
{
Console.Write($"{numbers[index]}\t");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}//end of DisplayArray

Testing the boolean search:
//Boolean search
Console.WriteLine($"Searching for 7 is {SearchArrayBoolean(numbers, PhysicalSize, 7)}");
Console.WriteLine($"Searching for 17 is {SearchArrayBoolean(numbers, PhysicalSize, 17)}");

Testing the location search:
//Location Search
Console.WriteLine($"Searching for 7's location is: {SearchArrayLocation(numbers,PhysicalSize,7)}");
Console.WriteLine($"Searching for 17's location is: {SearchArrayLocation(numbers, PhysicalSize, 17)}");

Testing the count search:
//Count Search
Console.WriteLine($"Count of how many 7's is {SearchArrayCount(numbers,PhysicalSize, 7)}");
Console.WriteLine($"Count of how many 17's is {SearchArrayCount(numbers, PhysicalSize, 17)}");

Test sorting the array:
DisplayArray(numbers, PhysicalSize);
//Sort the Array
SelectionSort(numbers, PhysicalSize);
Console.WriteLine("\nAfter the sort ...");
DisplayArray(numbers, PhysicalSize);
Test the Binary Search
//Binary Search
SelectionSort(numbers, PhysicalSize);
DisplayArray(numbers, PhysicalSize);
Console.WriteLine($"Binary search for 7's location is {BinarySearch(numbers,PhysicalSize, 7)}");
Console.WriteLine($"Binary search for 17's location is {BinarySearch(numbers, PhysicalSize, 17)}");