Arrays - 1D Arrays
Introduction
The first type of array you will learn is the 1D array (it is the most common).
Objectives
At the end of this lesson you will be able to:
- Declare a 1D array
- Load a 1D array
- Display a 1D array
How to Create an Array?
There are some things you need to know before you can create an array:
- What type of data will be stored: each element of the array must be of the same type of data
- How many elements: normally once an array is created it cannot be made to hold more elements than it was originally designed to hold
Once you know about an array you can give it a name: the naming follows the same naming conventions that we use for variables
Array Syntax
| Pseudo Code | Data Type | #Of Elements | C# Syntax |
| Declare age[6] As int | int | 6 | int[] age = new int[6]; |
| Declare mark[25] As double | double | 25 | double[] mark = new double[25]; |
| Declare name[100] As string | string | 100 | string[] name = new string[100]; |
| Declare gender[75] As char | char | 75 | char[] gender = new char[75]; |
Load Data Into an Array
There are several ways to load data:
- Declare the array with known data
- User/Program entered data
- From an external source such as a file (covered later)
Except for declaring the array with known data, the loading of data into an array involves looping; therefore, the size becomes very important
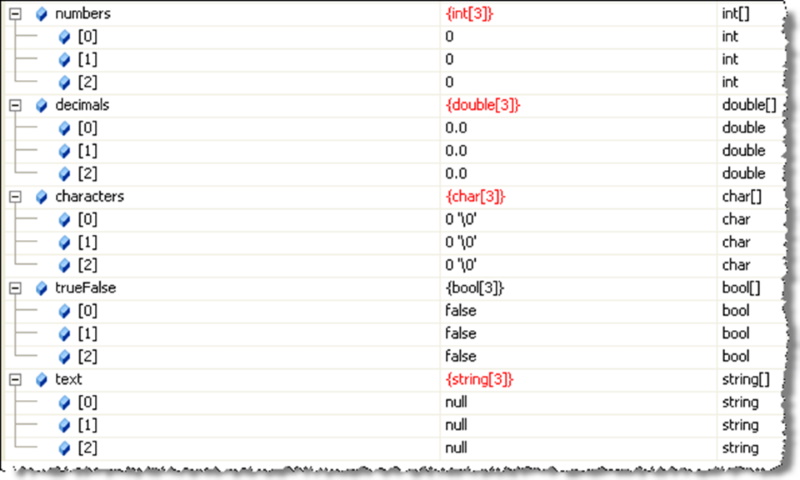
Default Array Values
Each type of array, once declared, has default values for each element:
Logical (filled) Size vs. Physical Size
- An array can be either completely full of data, or be only partially filled
- When an array is declared, given both size and data type, the computer only allocates a block of memory but does not give the elements any data; we must do that manually or programmatically
- Physical Size: the physical, declared, size of the array
- Logical (filled) Size: the number of elements with actual, known, data
Logical Size <= Physical Size
Manually Load Data
We can declare, and initialize, an array with pre-defined, known, data as shown below:
string[] dayOfWeek = {"SUN", "MON", "TUE", "WED", "THU", "FRI", "SAT"};
OR
int[] monthNumber = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 };
Question: How many elements are in each of these arrays?
Program Generated Array
Load an array with consecutive integer values:
// program generated array
int[] someNumbers = new int[10];
for (int index = 0; index < 10; index++)
{
someNumbers[index] = index;
}
OR
// create an array of random numbers from 1 to 100
Random random = new Random();
int[] randomNumbers[] = new int[10];
for (int index = 0; index < 10; index++)
{
randomNumbers[index] = random.Next[1, 101];
}
Question: What does the data in this array look like?
User Entered Data
You can have the user enter the data (the example below assumes the existence of the GetInteger() method:
// user entered data
int[] userEntered = new int[5];
for (int index = 0; index < 5; index++)
{
userEntered[index] = GetInteger("Enter an integer number: ");
}
Coding Practice
Coming soon…